Alkaline vs. Lithium Batteries
1 CommentBatteries are essential for keeping our devices running on portable power. The two popular types, alkaline and lithium batteries, have distinct characteristics that make them ideal for different uses. Understanding these differences allows you to select the best battery to ensure your devices operate smoothly and efficiently.
EVS Supply has been a trusted supplier of battery solutions from leading manufacturers. We carry a diverse selection of reliable batteries in various types and sizes, sourcing from the most reputable brands to ensure top-notch performance and longevity.
Alkaline Batteries
These batteries typically comprise zinc and manganese dioxide, serving as common disposable options. They function by converting chemical energy into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. Common applications include powering household items like remote controls, flashlights, and clocks.
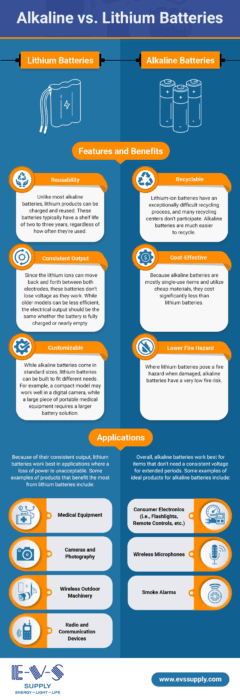
Features and Benefits of Alkaline Batteries
Here are the distinctive features and advantages of alkaline batteries:
- High energy output: Alkaline batteries provide a consistent and stable voltage output.
- Long shelf life: They can be stored for several years without significant loss of power.
- Wide availability: Alkaline batteries are readily available in various sizes and brands.
- Non-toxic: They do not contain heavy metals such as cadmium or mercury, which makes them safer for the environment.
- Cost-effective: They are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of batteries.
Ideal Applications of Alkaline Batteries
Listed below are various applications where alkaline batteries excel:
- Consumer electronics: Their long shelf life and consistent energy output make them perfect for devices with low, intermittent power demands, such as remote controls, flashlights, smoke alarms, and toys.
- Military and defense: Alkaline batteries’ reliability and lifespan make them ideal for other tactical gear, including high-frequency radios and GPS devices.
- Portable audio devices: These batteries provide stable power for wireless microphones, radios, CD players, and other portable audio equipment.
Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are made with lithium metal or compounds known for their high energy density and long lifespan. They function by moving lithium ions from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging. Common applications include powering smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
Features and Benefits of Lithium Batteries
The following describes the characteristics and benefits that differentiate lithium batteries:
- High energy density: Lithium batteries store more energy per unit weight than other battery types, making them ideal for portable electronics.
- Long lifespan: These batteries have a longer operational life and higher charge cycles.
- Low self-discharge: Lithium batteries retain their charge long when not in use.
- Lightweight: They are significantly lighter than other battery types with similar capacity.
- Durable: Their long lifespan reduces the frequency of battery replacements, which saves costs over time.
- Fast charging: They can be recharged quickly compared to other rechargeable batteries.
Ideal Applications of Lithium Batteries
Here are the several applications where lithium batteries prove highly effective:
- Smartphones and laptops: Their high energy density and long lifespan make them ideal for devices requiring frequent charging and high power.
- Industrial equipment: They are able to handle high-power demands, perfect for ground equipment, forklifts, conveyors, and more.
- Electric vehicles: These batteries areessential for providing long-lasting and efficient power to electric cars and other electric transport.
- Medical devices: Lithium batteries arereliable and durable, ideal for critical devices like pacemakers and portable medical equipment.
- Wearable technology: They have long battery life and lightweight properties and are perfect for fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other wearable devices.
EVS Supply: Your Premier Partner for Superior Alkaline and Lithium Batteries!
At EVS Supply, we provide high-quality alkaline and lithium batteries to meet all your power needs, along with a wide range of other battery options. Our offerings also include custom-built solutions tailored to your specific requirements, guaranteeing the perfect power solution every time.
Contact us now or request a quote to learn more about our offerings!